Credential Guard for Windows 11 & Windows Server 2025
Microsoft has announced that it will automatically enable Credential Guard for Windows 11 and Windows Server 2025, as long as the necessary prerequisites are met. In this article, you will learn what Credential Guard is, which prerequisites are required, and how you can ensure that all Windows machines in your network are protected by Credential Guard.
What is Credential Guard?
Credential Guard is a security feature integrated into Windows that uses Virtualization-based Security (VBS) to protect sensitive credentials such as NTLM hashes and Kerberos tickets. Via VBS, an isolated virtual environment is created on the system, which is then utilized by Credential Guard for storing this critical data. This isolated environment is accessible only to authorized processes and remains inaccessible to the rest of the system, enabling the protection of stored credential information even after the system has been compromised.
Sensitive Information beeing inaccessible by unauthorized processes makes it harder for attackers to extract information that can be used to execute NTLM (Pass-The-Hash) or Kerberos (Pass-The-Ticket) attacks. In practice, tools like Mimikatz can still bypass these protections, for example by using keylogging techniques to capture credentials after a system has been compromised. While Credential Guard does not eliminate all risks associated with credential theft, it remains a critical component of a defense-in-depth strategy for Windows system hardening. It is highly recommended for organizations looking to enhance the security of their domain environments.
Prerequisites for VBS / Credential Guard
The following prerequisites need to be met. This goes for physical clients as well as for virtual machines.
Supported Windows Version
Credential Guard is supported on following windows versions:
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Education
- Windows 11 Enterprise
- Windows 11 Education
- Windows Server 2016 and later
TPM Module
A TPM including TPM 2.0 needs to be available and enabled on the client / virtualization host for VBS to run.
Powershell command to check for an available TPM Module:
Get-Tpm
Secure Boot
Secure boot is required for VBS to run. For Virtual Machines, Secure Boot needs to be enabled on the Virtualization Host.
Powershell command to check for Secure Boot:
Confirm-SecureBootUEFI
Hardware-assisted virtualization
Vendor specific virtualization support like Intel-VT-x or AMD-V needs to be available and enabled on the client / virtualization host for VBS to run. Regarding Virtual Machines, nested virtualization typically needs to be manually enabled.
Powershell command to check for availability of virtualization support:
(Get-CimInstance Win32_Processor).VirtualizationFirmwareEnabled
How to enable VBS / Credential Guard
For Windows 10 and earlier versions of Windows Server, VBS and Credential Guard must be enabled through a GPO. However, starting with Windows 11 and Windows Server 2025, everything should be enabled by default as long as the necessary prerequisites are met.
The according GPO can be found at:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Device Guard > Turn On Virtualization-Based Security
How to check if VBS / Credential Guard is running
Currently, checking if VBS / Credential Guard is running must be done manually on each client. For large enterprises of course, this is a big drawback, as it makes verifying and maintaining such a critical security feature very hard to do.
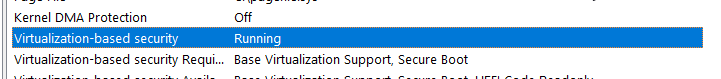
Check for Virtualization-Based Security (VBS)
If all of these prerequisites are met (TPM, Secure Boot, Virtualization Support) and it’s enabled via GPO (Pre Windows 11 / Windows Server 2025), VBS should be running on the system.
You can check for VBS running by using msinfo32.exe:
Check for Credential Guard
When checking for Credential Guard running, PowerShell is the most reliable method. Open PowerShell as an Administrator and enter the following command:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration -Filter "IPEnabled = 'True'" | ForEach-Object {
$_.SetTcpipNetbios(2)
}
pause
1 OR 1,2 OR 1,2,3 = Credential Guard is running
0 = Credential Guard is not running
If Credential Guard is not running, troubleshoot by verifying each prerequisite. In my experience, as long as all requirements are met, Credential Guard should work without any issues.
Sources
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/design/device-experiences/oem-vbs
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/identity-protection/credential-guard